【印刷可能】 concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere 198426-Concentration of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere
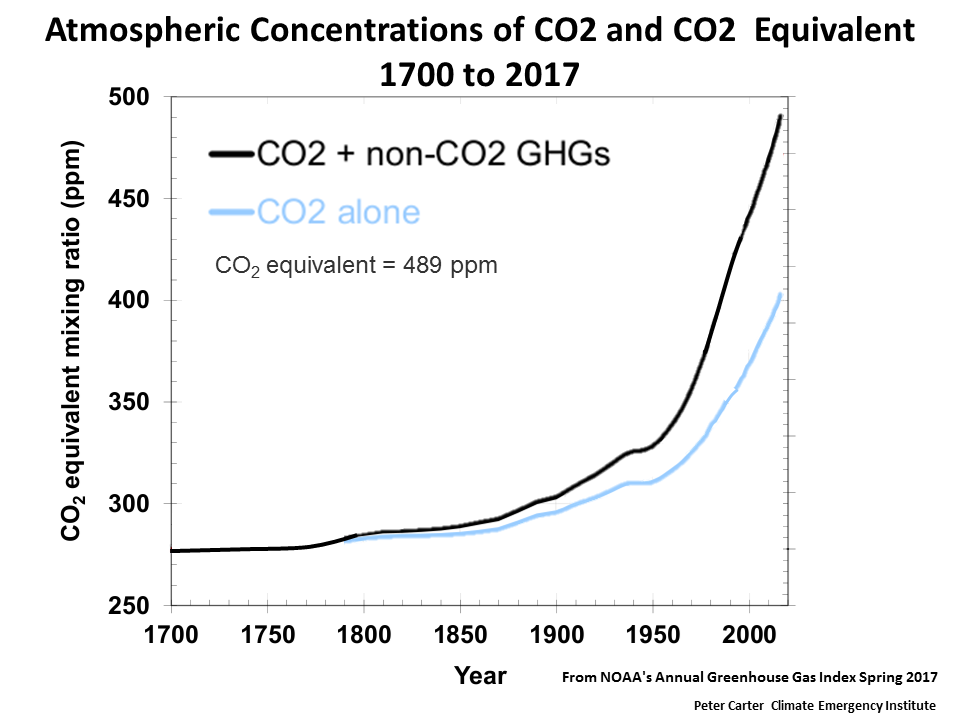
0 °C from 10 to 12 ( Stocker et al 13aIt took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from other gasesThese greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide is roughly the same no matter where you measure it Even though some countries produce more greenhouse gases than

Influence Of Greenhouse Gases To Global Warming On Account Of Radiative Forcing Intechopen
Concentration of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere
Concentration of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere-Greenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeHuman activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For example farming cattle releases methane




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm
Saw the highest concentration of greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere on record, along with unprecedented global sea levels and average global temperaturesThe largest greenhouse gas by volume is actually the one most people tend to overlook water vapor, whose concentration varies significantly depending on temperature As the temperature of the atmosphere increases, the amount of humidity in the atmosphere also goes up, further heating our planet in a vicious cycleThe concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere has increased in the last 0 years The extra carbon dioxide is causing an enhanced greenhouse effect, greater than
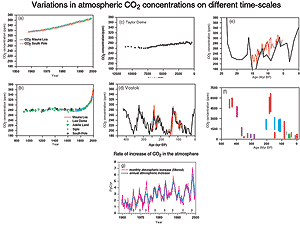
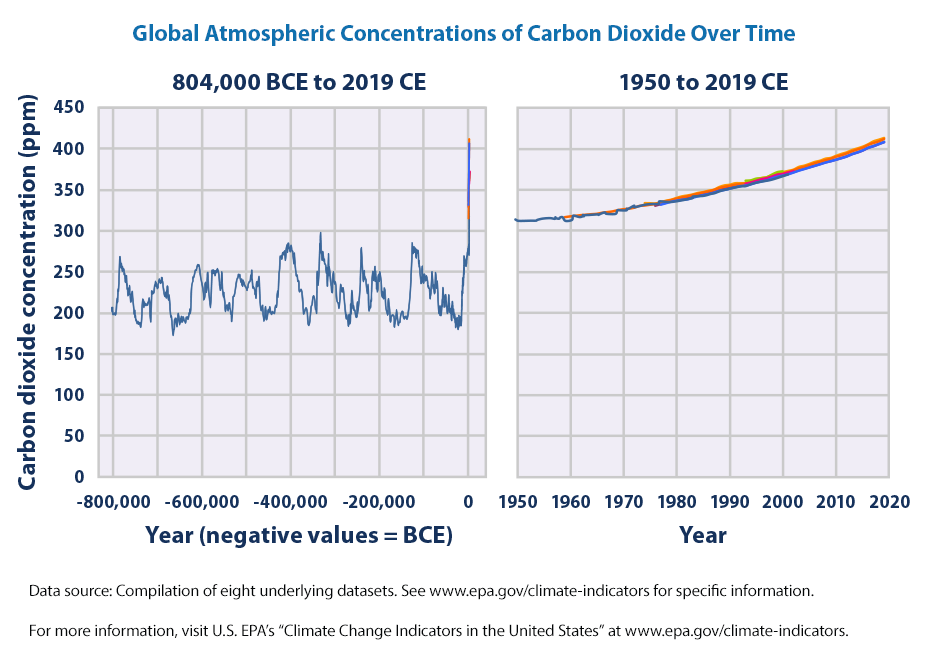
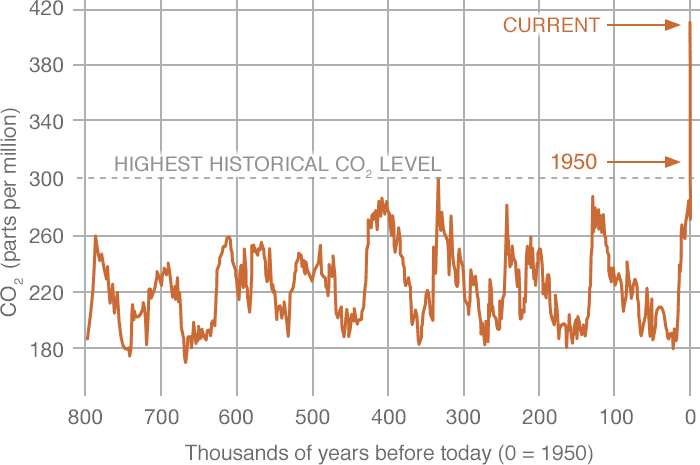
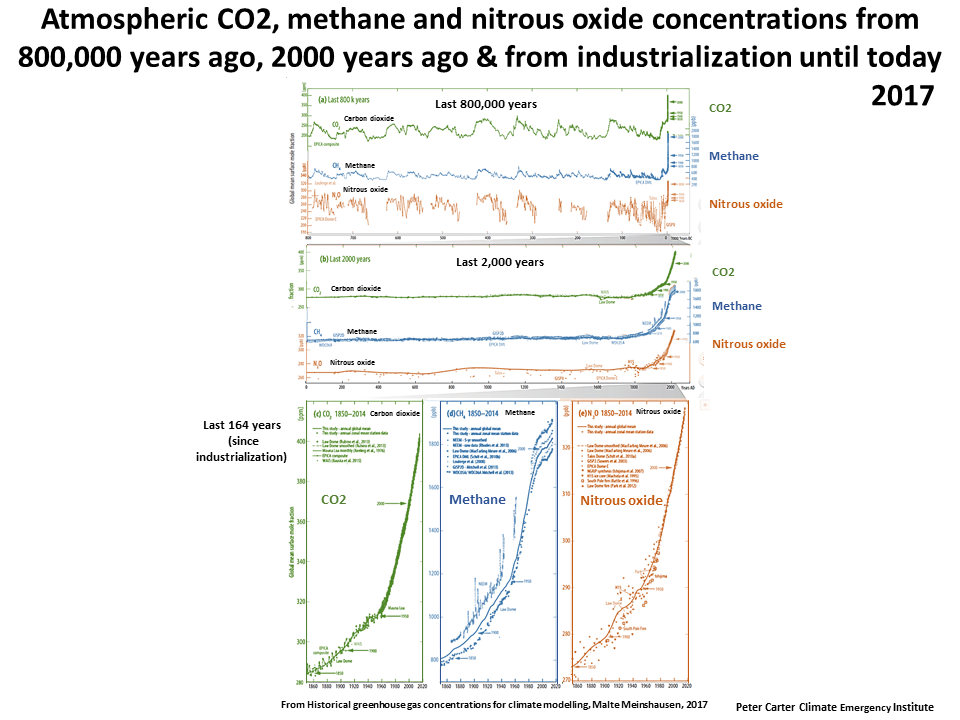
Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere Concentrations reached 4055 ppm in 17, 146% of the preindustrial era (before 1750) The increase inConcentration of greenhouse gases 18 June 19 Page 2 Investigating the concentration of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere over the last 800 000 years Ice core records provide the most direct and detailed way to investigate past climate and atmospheric conditions Ice cores are cylinders of ice drilled out of an ice sheet or glacierThe three most important greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4) and nitrous oxide (N 2 O) While carbon dioxide is the greenhouse gas we hear the most about, methane and nitrous oxide have greater global warming potential (GWP)Methane has a GWP of 25 for a 100year period and nitrous oxide has a GWP of 298
The AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990;The major Greenhouse Gas, carbon dioxide, emitted naturally and by the burning of fossil fuels, stays in the atmosphere a long time Its warming effect occurs even when the sky is clear and dry Climate scientists are so concerned about carbon dioxide because the more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, the hotter the earth will become, changingThe concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has been changing over the past 150 years Since preindustrial times atmospheric concentrations of the gases have increased CO 2 has climbed over 31 percent CH 4 has climbed over 151 percent N 2 O has climbed 17 percent



Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide




Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases From 0 To 05
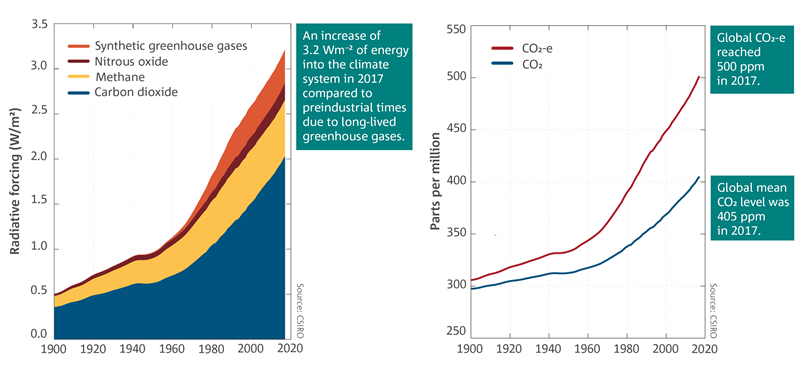
Measurements of greenhouse gases (GHGs), whether performed in the atmosphere, or over terrestrial or marine ecosystems, have led to a fundamental understanding of the Earth System during the last century Nevertheless, we still do not fully understand global greenhouse gas cyclingAs of 12, the warming effect of longlived greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere had increased by approximately 47% compared to 1990 Relative to preindustrial times, today's atmosphere absorbs an extra 3 watts of energy per square meterRecord high levels of greenhouse gas pollution continued to increase the heat trapped in the atmosphere in 19, according to an annual analysis released by NOAA scientists NOAA's Annual Greenhouse Gas Index tracks the concentrations of greenhouse gases being added to the atmosphere principally from humancaused emissions The AGGI then calculates the heat being added to Earth's atmosphere




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Greenhouse Gases Csiro
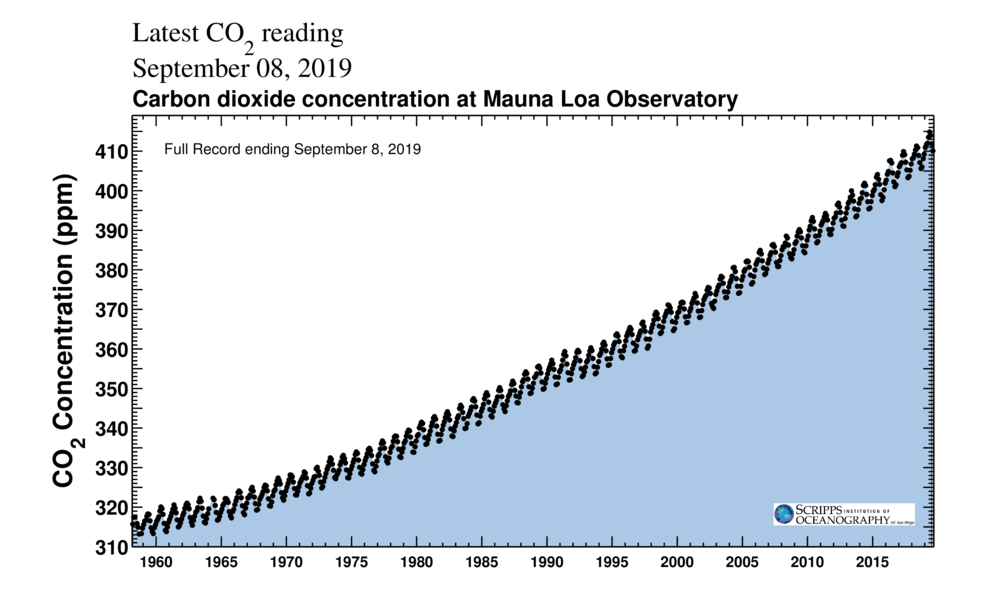
Greenhouse gases are gases—like carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane, and nitrous oxide—that keep the Earth warmer than it would be without themThe reason they warm the Earth has to do with the way energy enters and leaves our atmosphereWhen energy from the sun first reaches us, it does so mainly as lightHuman activities produce large amounts of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO 2), and thus contribute to global warmingThe use of fossil fuels is the primary source of CO 2 emissions, but the removal of trees from forested land has also contributed Mature forests, having absorbed CO 2 from the atmosphere while growing, store carbon in wood,The graphs show monthly mean carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii The carbon dioxide data on Mauna Loa constitute the longest record of direct measurements of CO 2 in the atmosphere They were started by C David Keeling of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in March of 1958 at a facility of the National Oceanic and



Changes In Concentration Of Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Other Greenhouse Gases And Aerosols




Those Who Worry About Co2 Should Worry About Methane Too The Economist
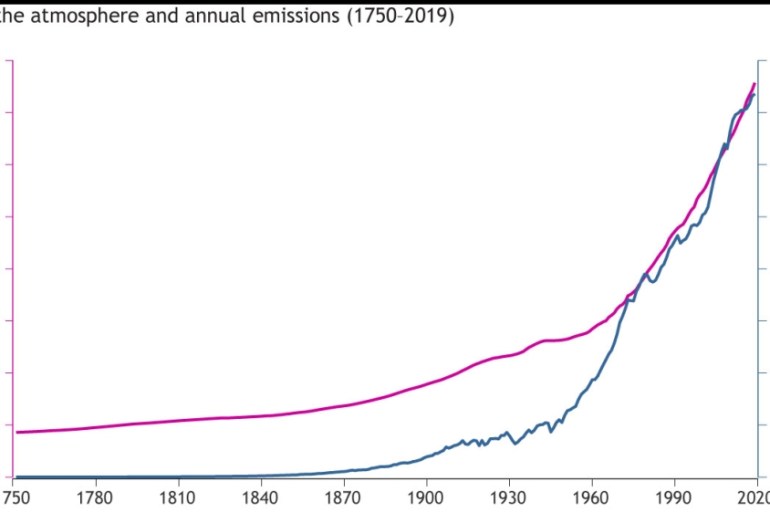
Greenhouse Gases and Temperature A greenhouse gas (GHG) is any gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation in the thermal infrared range These are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect, which results in increased temperatures on Earth The greenhouse effect occurs as the gases reach Earth's surfaceIn our work on CO 2 and Greenhouse Gases, we know that global emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide and other gases have increased rapidly over the past century, and particularly over the last 50 years We would expect that these emissions have changed the concentration of these gases in the atmosphere But how large has this effect been?The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect



Working Group I The Scientific Basis Get Javascript Other Reports In This Collection C 1 Observed Changes In Globally Well Mixed Greenhouse Gas Concentrations And Radiative Forcing Over The Millennium Before The Industrial Era The Atmospheric



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, been increasing the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases (mainly carbon dioxide and methane) above the natural amount, which has led to increased warmingEffects of increased greenhouse gases The growing concentrations of humangenerated GHGs have resulted in an increased absorption, largely in the lower atmosphere, of the heat radiated from Earth's surface, causing an increase in the global (land and ocean) mean surface temperature of 085 ±This imbalance between greenhouse gas emissions and the ability for natural processes to absorb those emissions has resulted in a continued increase in atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere have increased by about 40% since the mid1800s




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



Whole Atmosphere Mean Ghg Concentration Greenhouse Gases Observing Satellite
Concentrations of greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere hit a record high this year, a United Nations report showed on Wednesday, as an economic slowdown amid the coronavirus pandemic hadGlobal warming Greenhouse effect Since the industrial revolution, the concentration of greenhouse gases has been steadily growing There is now a reasonable consensus that this will produce an increase in the heat trapped in the atmosphere and consequently a global climate change The more likely changes are shifting of climatic zones and aThe concentration of water vapor (a greenhouse gas) varies significantly from around 10 ppm by mole fraction in the coldest portions of the atmosphere to as much as 5% by mole fraction in hot, humid air masses, and concentrations of other atmospheric gases are typically quoted in terms of dry air (without water vapor)
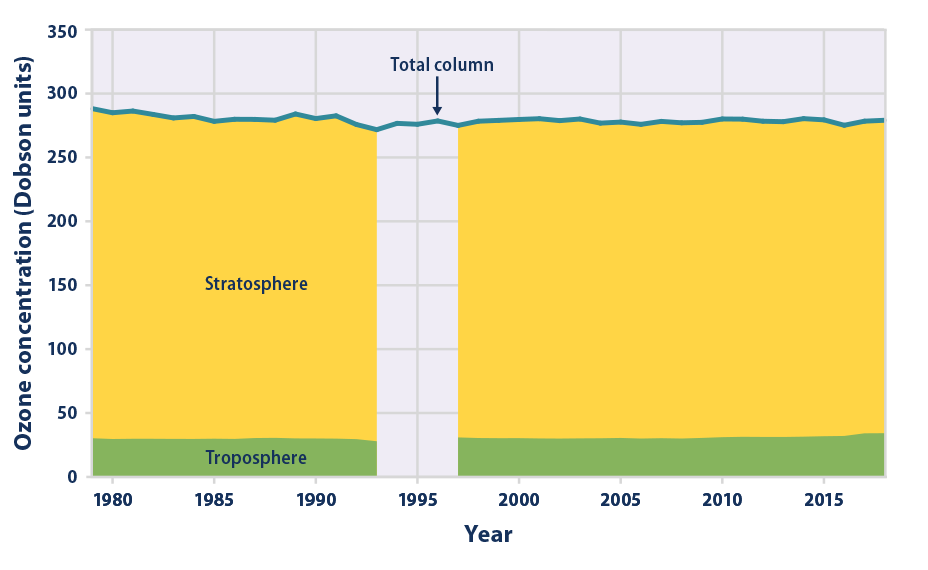



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Carbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147% of preindustrial level in 1750 The increase in CO2 from 17 to 18 was above the average growth rate over the last decade The growth rate of CO2 averaged over threeA greenhouse gas is a gas in the atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation This is causing a greenhouse effect, and the resultant warming of the earth's surface to a temperature above its normal temperature range The radiation is released and redirect towards the earth surface depends on a number of greenhouse gasses in the atmosphereCarbon dioxide is the main longlived greenhouse gas in the atmosphere related to human activities Its concentration reached new highs in 18 of 4078 ppm, or 147 percent of preindustrial level



1




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,The enhanced greenhouse effect What has scientists concerned now is that over the past 250 years, humans have been artificially raising the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere at an everincreasing rate, mostly by burning fossil fuels, but also from cutting down carbonabsorbing forestsThe naturally occurring gases in the atmosphere, showing where the highest concentration of gases are and the percentages of each accurately The greenhouse gases in the atmosphere (rememberthese are also naturally occurring – just in a harmful percentage) Each continent and the areas of highest global emission within The Ozone Hole




Topic 1 Observed Changes And Their Causes Ipcc




2 Global Averaged Atmospheric Concentrations Of The Greenhouse Download Scientific Diagram
Too much greenhouse effect The atmosphere of Venus, like Mars, is nearly all carbon dioxide But Venus has about 154,000 times as much carbon dioxide in its atmosphere as Earth (and about 19,000 times as much as Mars does), producing a runaway greenhouse effect and a surface temperature hot enough to melt leadGreenhouse gases are gases in the Earth's atmosphere that produce the greenhouse effect Changes in the concentration of certain greenhouse gases, from human activity (such as burning fossil fuels), increase the risk of global climate change Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane, nitrous oxide, halogenatedEven if greenhouse gas concentrations stabilized today, the planet would continue to warm by about 06°C over the next century because of greenhouses gases already in the atmosphere See Earth's Big Heat Bucket, Correcting Ocean Cooling, and Climate Q&A If we immediately stopped emitting greenhouse gases, would global warming stop?




Greenhouse Effect And Historical Emissions




Greenhouse Gases Bioninja
Ozone is also a greenhouse gas, but it differs from other greenhouse gases in several ways The effects of ozone depend on its altitude, or where the gas is located vertically in the atmosphere Most ozone naturally exists in the layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere, which ranges from approximately 6 to 30 miles above the Earth'sCarbon dioxide Carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the single most important greenhouse gasIt is responsible for approximately 65 % of the radiative forcing that is currently observedThe additional greenhouse gases are contributing to global warming and to associated climatic changes The global average concentration of water vapour quickly rises in response to an increase in global temperature, due to the increased waterholding capacity of a warmer atmosphere




Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Latest Information On Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Makes For Chilling Reading Environmental Pollution
Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe link between greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and warming temperatures is clear CO 2 is continuously exchanged between the land, the air, and the ocean While more than half of emitted CO 2 is removed from the atmosphere through natural processes within a century, about percent remains in the atmosphere for many millenniaAtmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations Concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere have risen over time Levels are expected to remain highfor many generations Rising global temperatures are directly linked to increased concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere These gases warm the Earth's surface by trapping heat
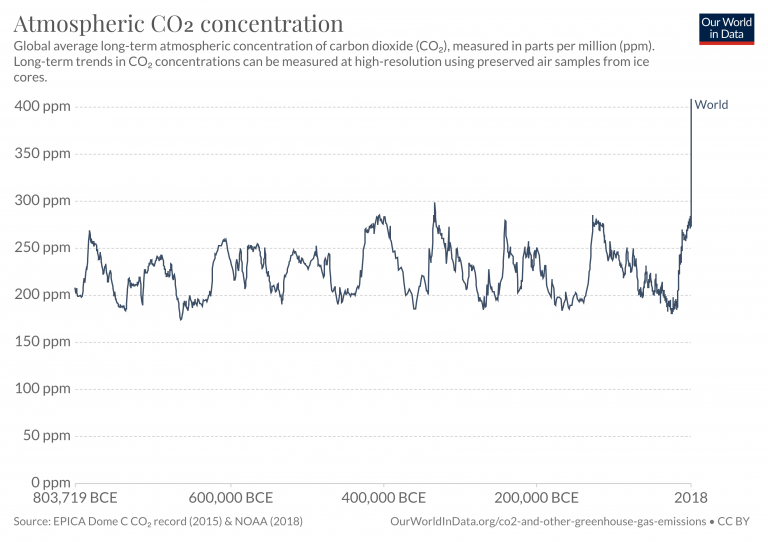



Atmospheric Concentrations Our World In Data
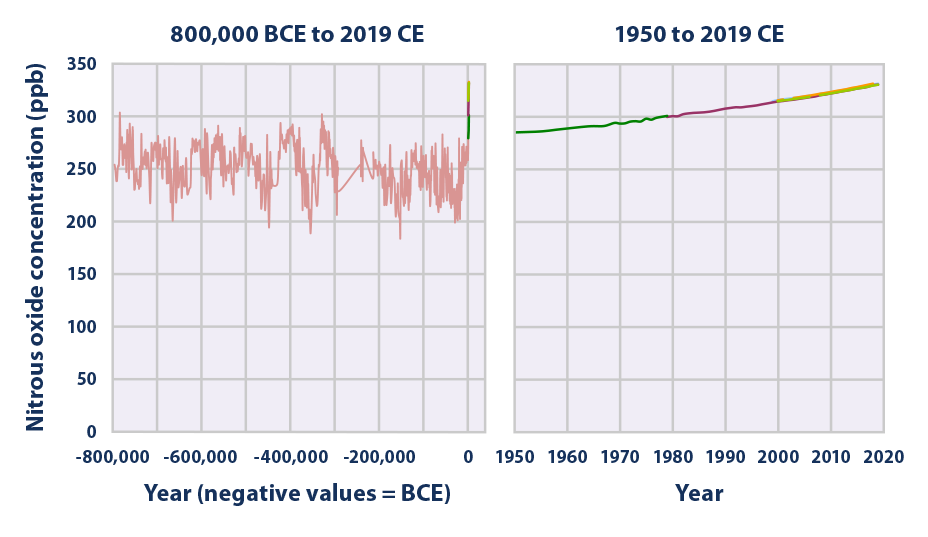



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
These problems have arisen due to the increase in Greenhouse gases (GHGs) concentration in the atmosphere Most of the factors responsible for GHGs emissions are anthropogenic such as fossil fuel combustion, biomass burning, etc Nature has developed its own way of fighting the GHGs problem by evolving microorganisms responsible forAnswer 2 on a question A greenhouse gas that has the highest concentration in the atmosphere the answers to realanswersphcom




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



Atmo336 Spring 21




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm




Solved Increasing The Concentration Of Greenhouse Gases In Chegg Com




Despite Pandemic Shutdowns Carbon Dioxide And Methane Surged In Welcome To Noaa Research




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency
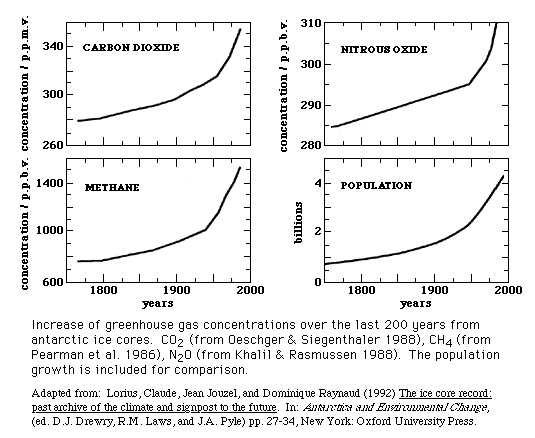



V1003 Science And Society Sources And Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Copernicus
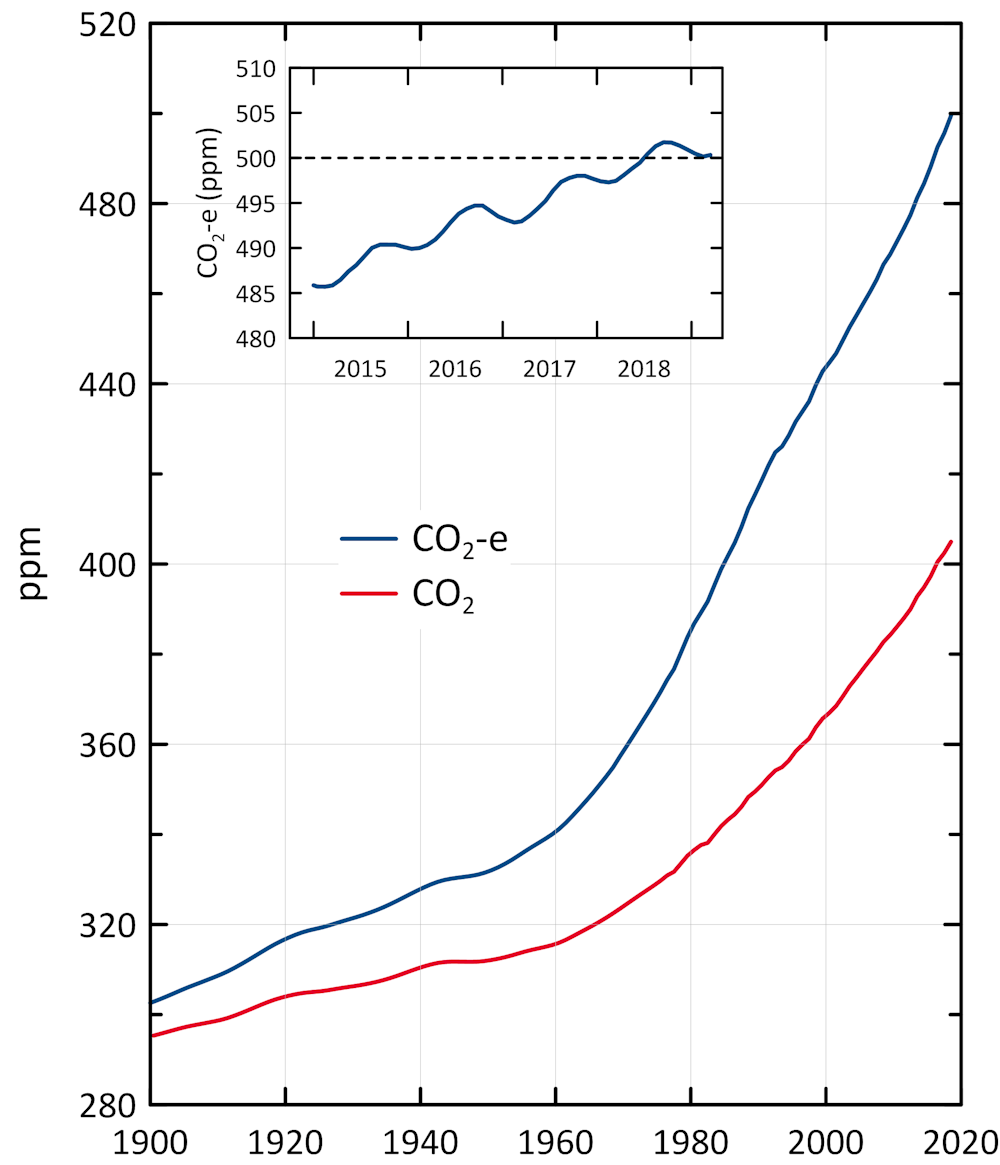



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



The Greenhouse Effect
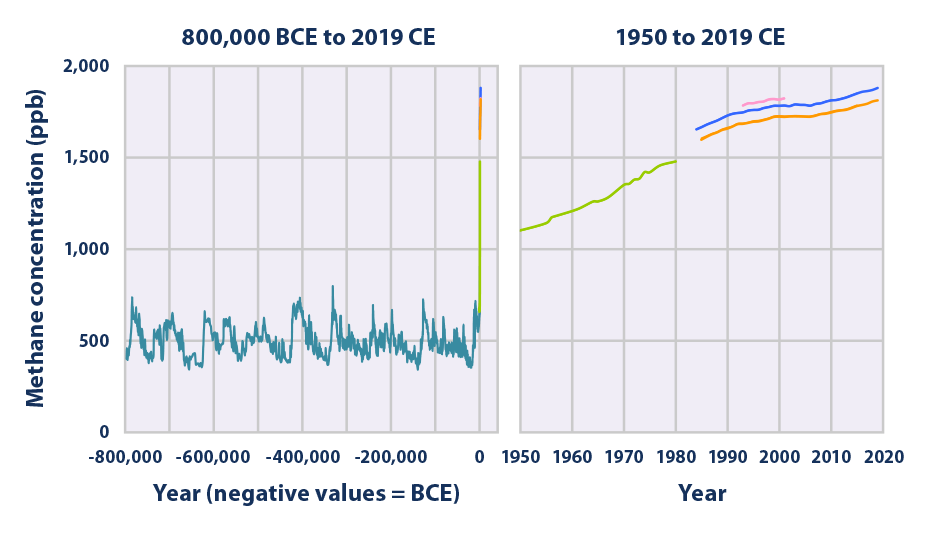



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
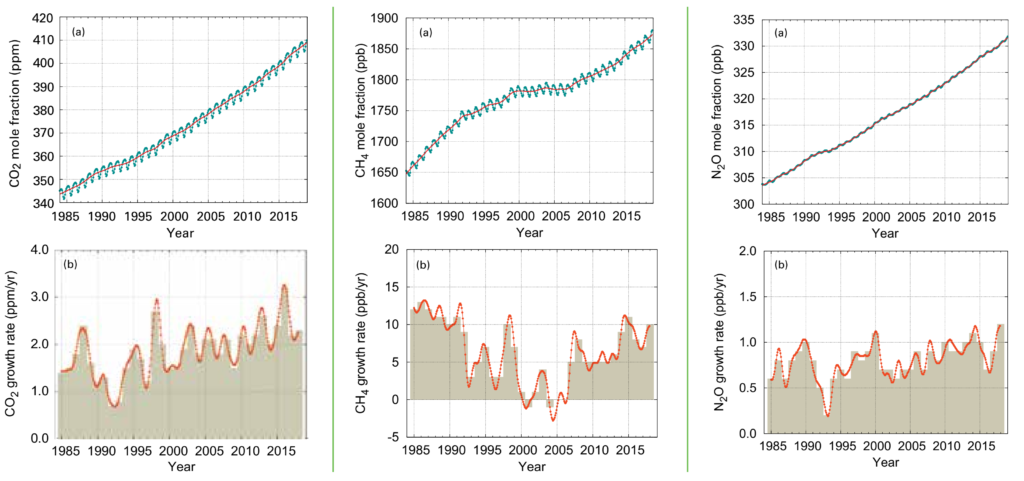



Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reached Yet Another High In 18 Desdemona Despair



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Atmospheric Concentration Of The Major Anthropogenic Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Reach New Record World Meteorological Organization



Annual Ghg Index Aggi



Atmospheric Concentrations Fluorocarbons




On Strategies For Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Pnas




Influence Of Greenhouse Gases To Global Warming On Account Of Radiative Forcing Intechopen



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
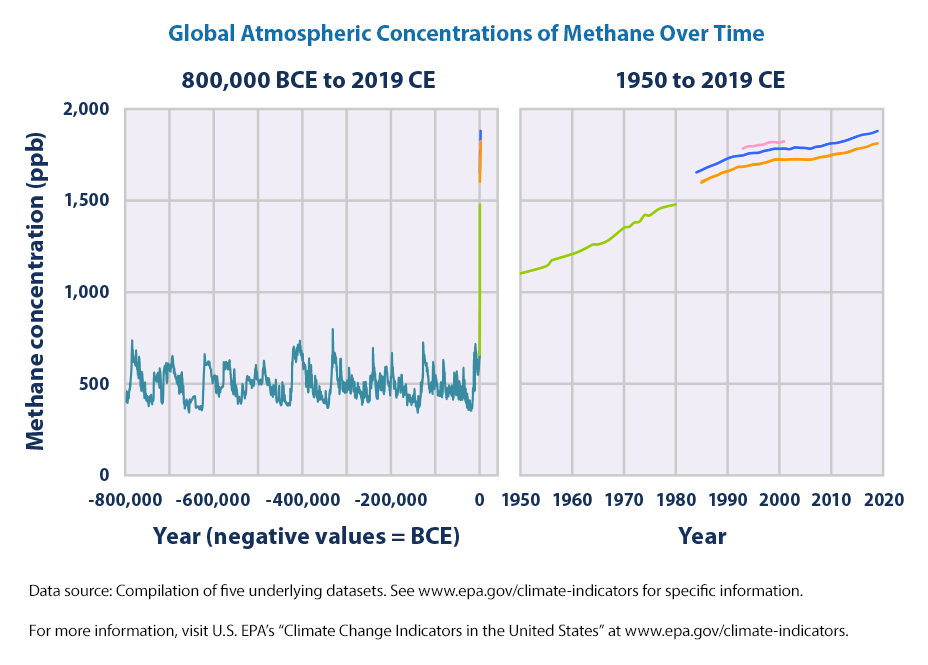



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Atmospheric Concentrations Our World In Data




Climate Change The State Of Our Atmosphere Climate Change News Al Jazeera



Carbon Dioxide Vital Signs Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



Untitled Document



The Greenhouse Effect



Ozone Layer




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research



Atmospheric Concentrations Fluorocarbons




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization



Co2 Makes Up Just 0 04 Of Earth S Atmosphere Here S Why Its Impact Is So Massive



Greenhouse Gas Basics 148 Msu Extension




Usgcrp Indicator Details Globalchange Gov




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Atmosphere Reach Yet Another High World Meteorological Organization




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Annual Ghg Index Aggi




Methane And Greenhouse Gases Atmospheric Chemistry And Global Change Research Group




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Climate Change The State Of Our Atmosphere Climate Change News Al Jazeera



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Surge To New Record World Meteorological Organization



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gases



1



The Greenhouse Effect Pveducation
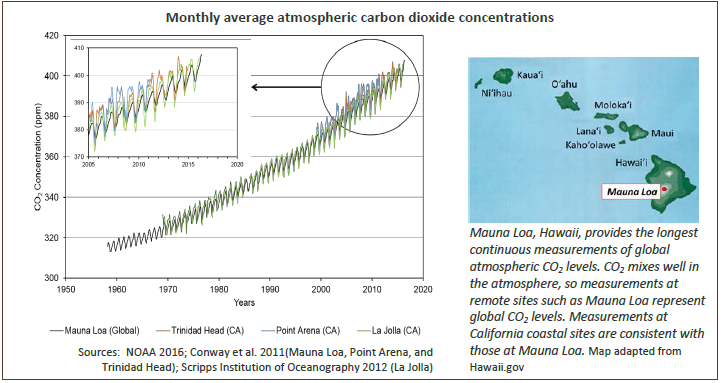



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Oehha
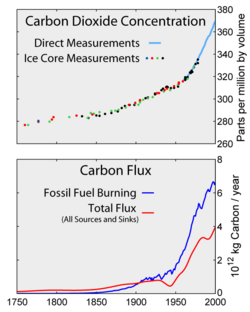



Greenhouse Gas New World Encyclopedia



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency




Atmospheric Concentrations Of Important Long Lived Greenhouse Gases Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations In Highest Ever Recorded Npr




Nonlinearity And Overlap In The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
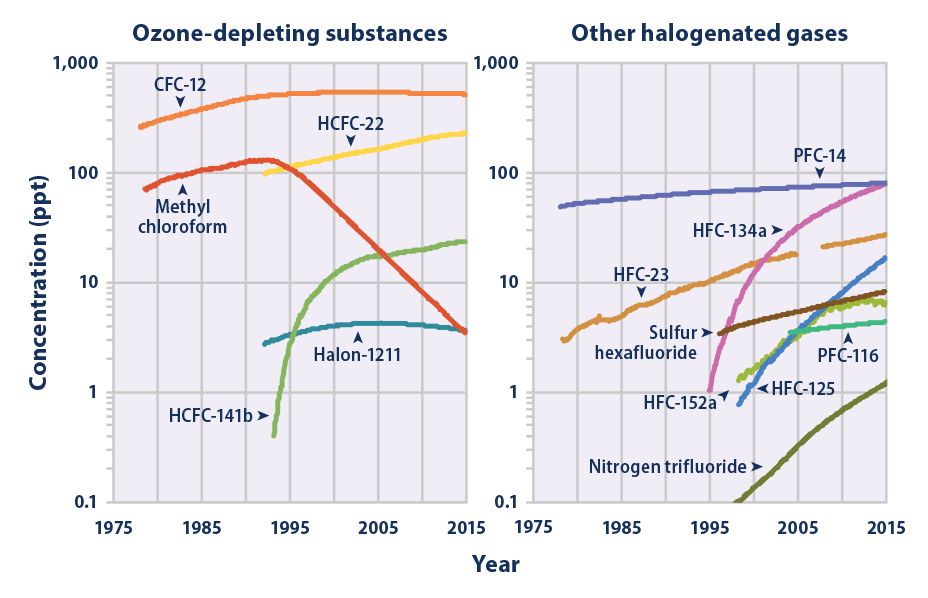



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
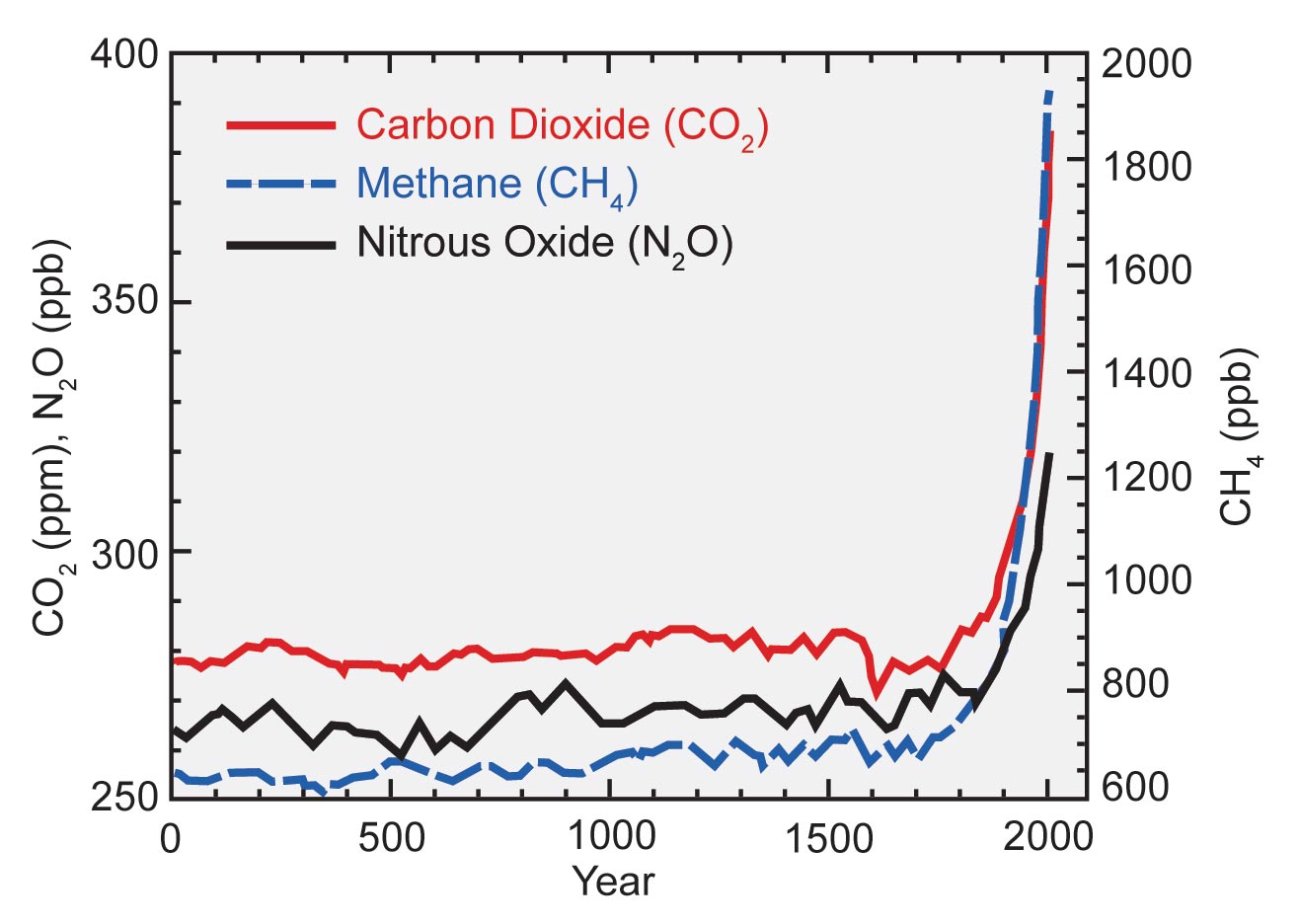



Climate Literacy Quiz



Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Concentrations European Environment Agency



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
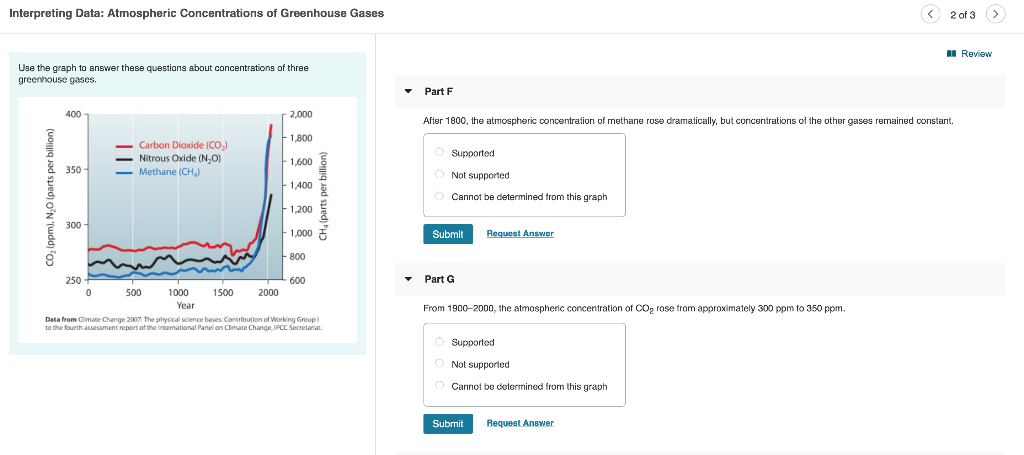



Solved Ch 18 Interpreting Data Atmospheric Concentrations Chegg Com




Global Warming




Are Humans Causing Or Contributing To Global Warming Noaa Climate Gov



3
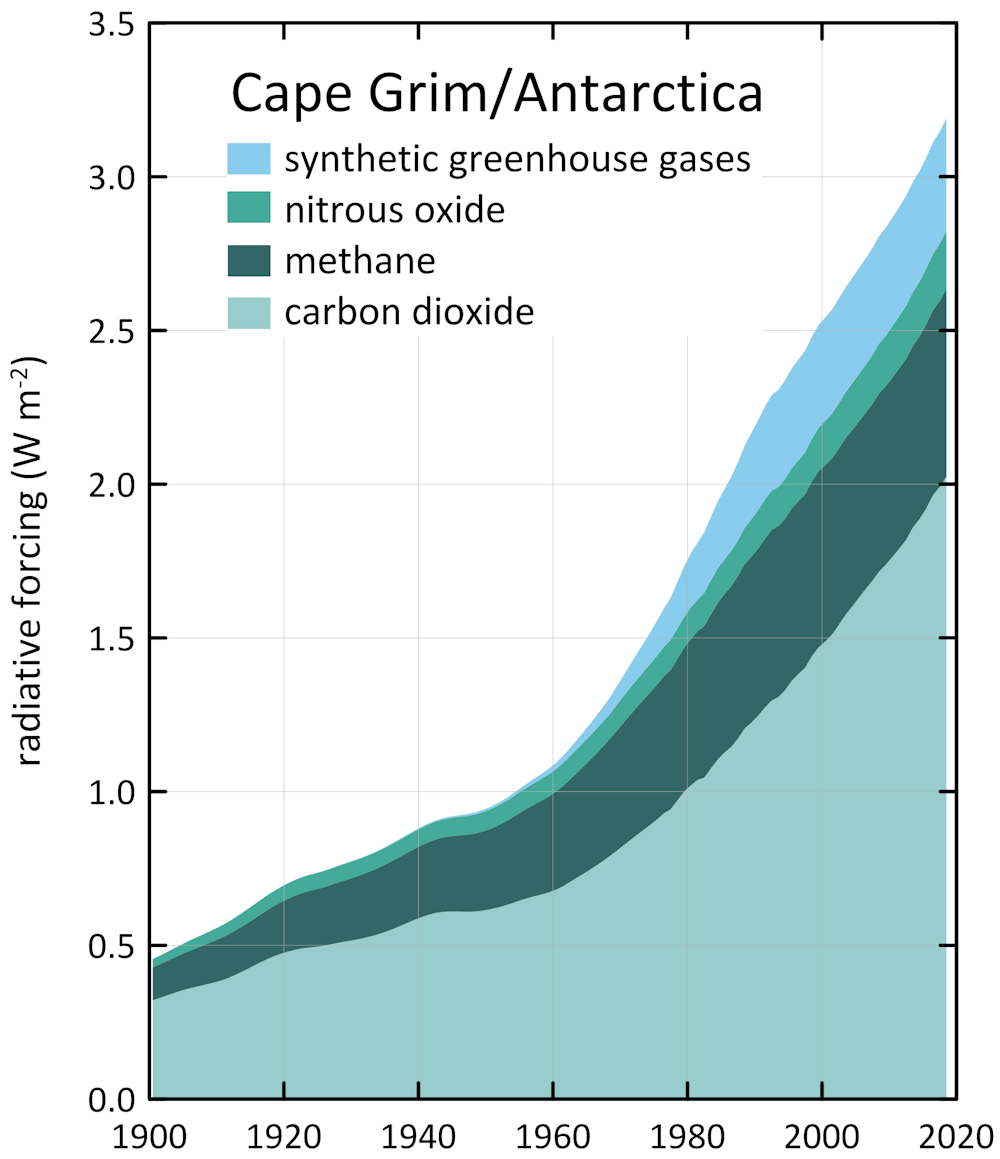



Why There S More Greenhouse Gas In The Atmosphere Than You May Have Realised
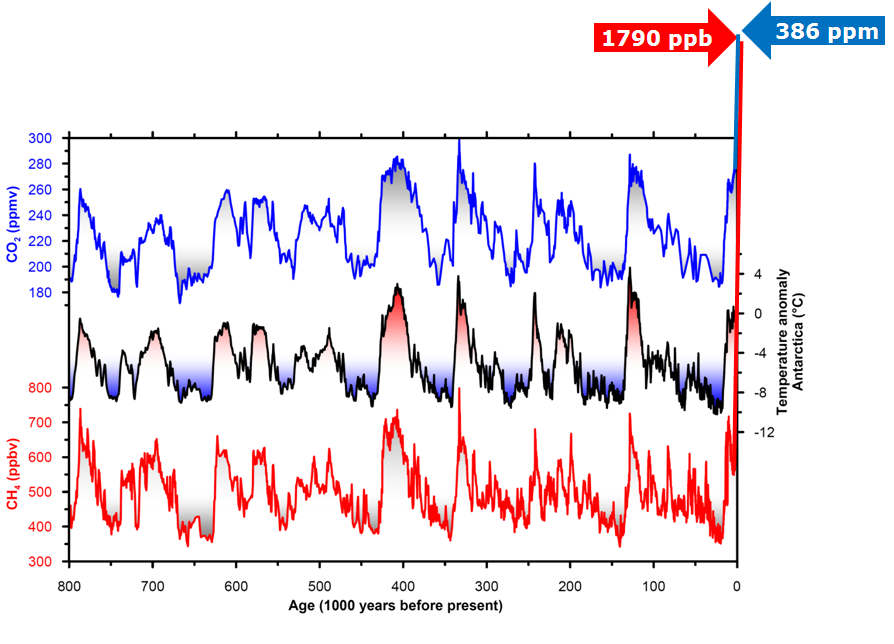



Past Atmospheric Composition And Greenhouse Gases University Of Copenhagen




Global Warming Radiative Forcing Britannica




Atmospheric Concentrations Of The Three Main Greenhouse Gases Carbon Download Scientific Diagram
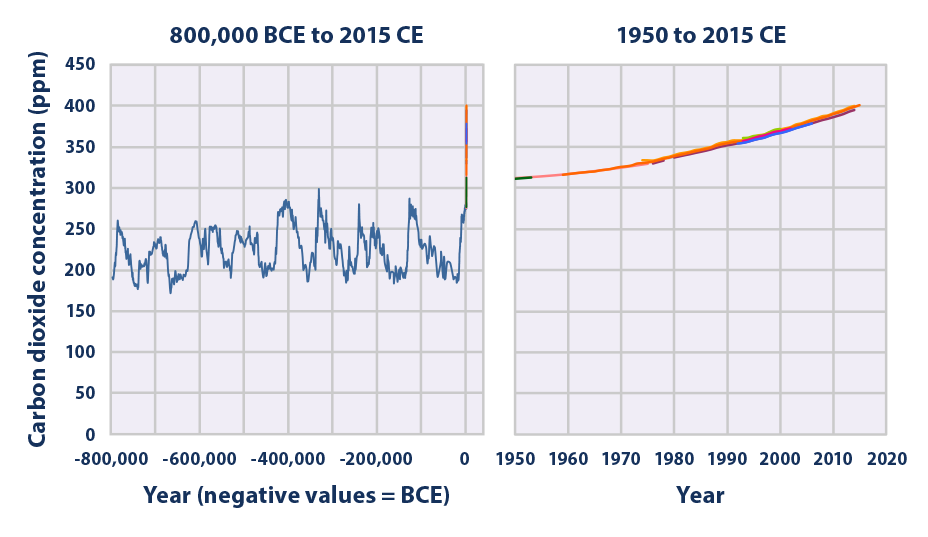



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Climate Change Indicators In The United States Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Greenhouse Gases And Temperature
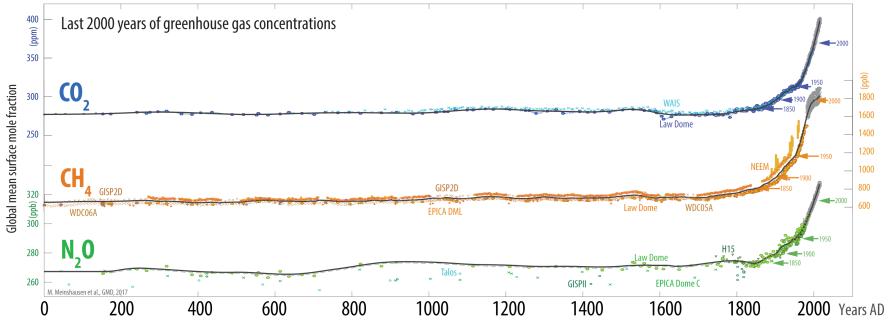



Key Greenhouse Gases Higher Than Any Time Over Last 800 000 Years Pursuit By The University Of Melbourne




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Concentrations Hit Record High Ecowatch



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming
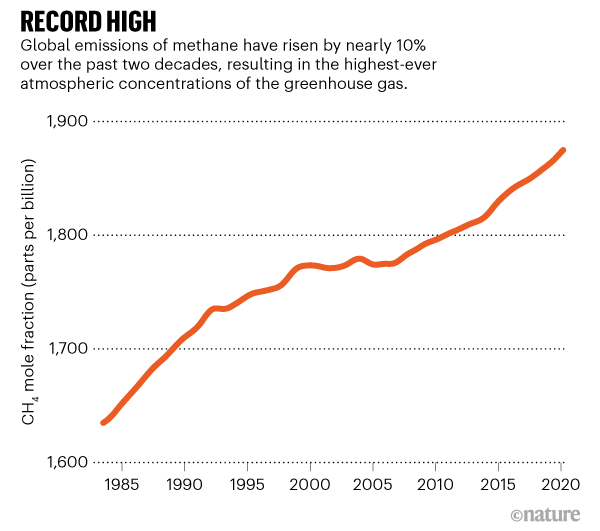



Global Methane Levels Soar To Record High
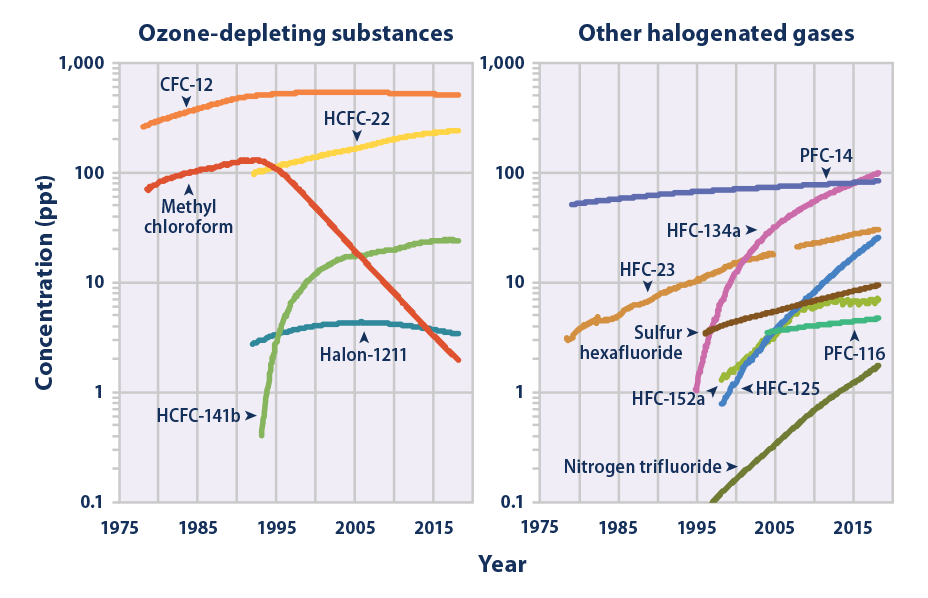



Climate Change Indicators Atmospheric Concentrations Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
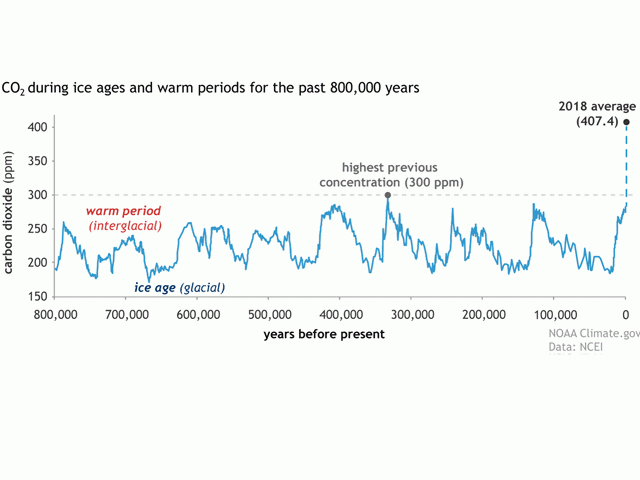



New Record Level Of Greenhouse Gas




If Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases Were Stopped Would The Climate Return To The Conditions Of 0 Years Ago Royal Society




Greenhouse Gas Levels In Atmosphere Hit New High Un
コメント
コメントを投稿